What is Market Share, and Why Should We Care?

What is Market Share?
Market share measures how much of the market a particular company controls compared to its competitors. It’s shown as a percentage and tells us a lot about the size and competitiveness of a company in its market.
Why is Market Share Important?
Understanding a company’s market share is like knowing who is leading the race in a specific industry. It shows which companies are doing well and which ones might be struggling. This info is especially useful for businesses looking to expand or improve their strategies.
Fundamentals of Market Share
How is Market Share Calculated?
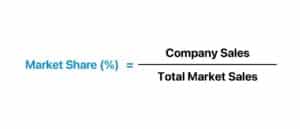
Calculating market share is pretty straightforward:
First, find out the company’s total sales over a certain period.
Then, get the total sales of the entire industry during the same period.
Finally, apply the market share calculation: (Company’s Total Sales / Industry’s Total Sales) × 100.
This percentage tells you how big of a slice of the market the company holds. You can look at this through different lenses—like revenue market share, which focuses on money made, or unit sales, which looks at the number of items sold.
What Influences Market Share?
Several factors can change a company’s market share:
- Industry-specific dynamics: Different industries have different factors that can affect market share. For example, tech companies heavily depend on innovation, while fashion brands might rely more on marketing.
- Competitive environment: If many companies are competing for the same customers, the market share can change quickly. Companies need to stay sharp and adapt to keep or grow their share.
Types of Market Share
- Overall market share: This is the big-picture view, showing a company’s position in the entire market.
- Segment market share: This breaks things down into smaller parts, like a company’s share in a specific product category or demographic.
- Geographic market share: This tells us how a company is doing in different areas, which is crucial for businesses operating in several regions.
Understanding these different types can help a company focus its efforts more effectively. For example, a business might have a strong overall market share but could do better in certain areas or segments.
Keeping an eye on market share data, including sales growth and market share percentage, helps a company understand where it stands in the total market.
Market Leader vs. Market Followers
Market leaders—those firms that command the highest market share within their industries—often dictate market trends and are considered benchmarks. Their dominance is reflected in high unit sales, which not only boost their visibility but also enhance their ability to strengthen customer relationships.
Industry reports frequently highlight these companies as primary influencers within their sectors, whether it be in the smartphone industry or any other tech-driven field.
Entering a market where established players hold significant market share can be a big challenge for new companies. These incumbents often possess deep customer loyalty, built over years of reliable service and customer relationships, making it harder for new entrants to lure away loyal customers.
Additionally, these market leaders might have the capital to invest in new technology, further raising the barriers to entry.
How Dominant Players Use Market Share to Their Advantage
Dominant companies leverage their market share to exert considerable influence over the entire industry. This can include lowering prices to outcompete smaller rivals temporarily, or scaling operations to reduce costs per unit, showcasing how market data supports strategic decisions that keep them ahead.
The Relationship Between Market Share and Profitability
Economies of Scale and Scope
The greater the market share, the more a company can achieve economies of scale. This cost advantage is often reflected in the pricing authority these companies command, enabling them to maintain or increase profitability by spreading costs over a larger output.
Market Power and Pricing Authority
With a substantial market share, a company often gains pricing authority which can deter new entrants and influence the pricing strategies across the entire industry. Market leaders use this power to optimize profitability, which can be crucial when competitors attempt to lose market share by aggressive pricing or other strategies.
By carefully analyzing market share and applying the market share formula (Market Share = Company Sales / Total Industry Revenue x 100), companies can gauge their influence and strategy effectiveness continually.
Market Share Analysis Techniques
Methods for Estimating Market Share
Market share represents a crucial key indicator in assessing a company’s stature within its industry, reflecting its competitive edge and capacity for influencing market dynamics. Here are established methods for estimating market share:
- Historical Sales Data Analysis: Analyzing historical sales data offers insights into trends and patterns over a designated period. This approach helps companies identify the phases during which their market share expanded or contracted with direct competitors. By examining the sales during the same period across different years, companies can deduce the effectiveness of their strategies and how key decisions, like lowering prices, impacted their market position relative to their biggest competitor.
- Surveys and Market Research: Engaging current customers through surveys and detailed market research provides a deeper understanding of market needs and customer preferences. This method helps in determining a company’s share by analyzing customer loyalty, the potential for repeat purchases, and the extent to which product innovation attracts new customers. Market research also gauges the target audience’s responsiveness to pricing strategies, which can compel companies to adjust their tactics to either raise prices or force competitors to lower theirs, impacting overall market dynamics.
Tools and Resources for Market Share Analysis
Advancements in technology have equipped businesses with sophisticated tools and resources to refine their market share analysis.
Various analytical software and extensive databases have become indispensable tools for companies aiming to expand their customer base and increase their market share. These resources allow for the detailed tracking of total revenue and sales performance in comparison to industry leaders.
They are also key in monitoring stock performance, which is often seen as a reflection of a company’s success in maintaining or increasing its market share. By leveraging these tools, companies can strategically position themselves to improve profitability and exert a significant impact on the market.
Strategic Importance of Market Share
Strategic Decisions Influenced by Market Share
Market share, defined as the percentage of total sales or revenue generated by a company within a specific period in a given industry, plays a crucial role in strategic corporate decisions. It serves as a useful metric for guiding investment, marketing, and resource allocation decisions.
Companies rely on market share data to gauge their performance against competitors, identify growth opportunities, and strategize on entering new demographics.
Market Share and Business Growth
Increasing market share is synonymous with growing a business. As a company captures a larger portion of the market, it often enjoys economies of scale which lead to reduced costs and increased profitability. A higher market share can also enhance a company’s influence within the industry, allowing it to set trends and standards that shape market dynamics.
The drive to increase market share can lead to innovative products and services, thereby attracting more customers and boosting revenue.
Challenges in Growing Market Share
Growing market share is not without its challenges. Competitors may respond aggressively, leading to a potential price war which can affect profitability. Additionally, market saturation occurs when a significant portion of potential customers has already been captured, making further growth challenging.
This is particularly true for well-established companies operating on a greater scale. They must find innovative ways to attract new demographics or enhance value to retain their market share over time periods.
Case Studies
Example 1: Dominance in the Technology Sector
In the technology industry, brands like Apple and Samsung have maintained the highest market share through strategic innovation and extensive advertising campaigns. Their ability to offer cutting-edge technology and reliable consumer electronics at competitive prices has allowed them to expand their consumer base and increase market share consistently over time.
By analyzing industry sales data and consumer preferences, these companies strategically place their products to maximize visibility and appeal, enhancing both profitability and revenue.
Example 2: Changes in Market Share in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has seen significant shifts in market share due to the advent of electric vehicles (EVs). Traditional automakers have experienced changes in their market shares as companies like Tesla have introduced innovations that cater to the growing demand for environmentally friendly transportation options.
The impact of electric vehicles is reshaping market dynamics, where the percentage of industry sales attributed to electric vehicles continues to grow, influencing the profitability and strategic decisions of longstanding automotive brands.
Example 3: The Rise and Fall of Market Leaders in Retail
Retail giants like Walmart and Amazon exemplify how dominant players can influence market share dynamics within the retail sector. These companies leverage their extensive distribution networks and competitive pricing strategies to capture and retain a significant percentage of market share.
Their practices of analyzing consumer data to tailor the shopping experience and using aggressive advertising strategies have enabled them to maintain their status as market leaders, even as the retail landscape evolves.
Future Trends Affecting Market Share
Technological Innovations
The ongoing digital transformation, including the integration of AI technologies, is continually reshaping market dynamics across various industries. Companies that embrace these technologies tend to see an increase in market share by improving consumer engagement and operational efficiencies, which in turn can lead to higher revenue generation over time.
Global Economic Factors
Global events and economic shifts play a crucial role in influencing market share. Factors such as economic recessions or expansions, trade policies, and international conflicts can lead to significant fluctuations in market shares as companies adjust their strategies to navigate these changes.
Consumer Behavior Trends
Shifts in consumer preferences significantly impact market dynamics. A greater scale of data collection and analysis allows companies to anticipate and react to these trends, expanding their market share by aligning their product offerings with consumer expectations and thereby enhancing brand loyalty and profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is relative market share and why is it important?
Relative market share compares a company’s market share to that of the largest industry leader. This metric helps companies understand their competitive position within a relative market, guiding strategic decisions to improve their standing over a specific time period.
How is relative market share calculated?
The relative market share formula involves dividing a company’s market share by the market share of the industry leader. This provides insight into how close a company is to becoming the leading brand within their target audience and relative market.
How can companies protect their market share?
Companies protect their market share by strengthening customer relationships and ensuring consumer loyalty. This approach helps maintain a stable revenue stream and discourages consumers from switching to competitors, even if competitors offer lower prices.
Why do industry leaders often offer lower prices?
Industry leaders may offer lower prices to attract a broader target audience and deter new entrants into the market. By leveraging economies of scale, they can afford to reduce prices while maintaining profitability, further securing their position as the market leader.
What benefits does a company gain as it increases its market share?
As a company increases its market share, it gains significant advantages such as increased consumer visibility and enhanced bargaining power. This allows for better negotiations with suppliers and can lead to lower costs and increased profitability over a defined time period.
What are the Best ASX Stocks to invest in right now?
Check our buy/sell tips

Recent Posts
Geopolitics, AI, and Energy, The Three Pillars of Investment Growth in 2026
Investing right now feels riskier than ever – messy geopolitics, the AI boom, and power shortages are all piling on.…
ReadyTech (ASX:RDY) Down 57%, Where’s the Operating Leverage?
ReadyTech Soft Half Keeps Pressure on the Stock ReadyTech has had a rough 12 months. The stock has fallen from…
Adisyn (ASX:AI1) Graphene Makes Drones Harder to Detect
Big Step in Drone Stealth With Graphene Adisyn (ASX:AI1) has successfully completed an early proof of concept demonstrating that graphene…


